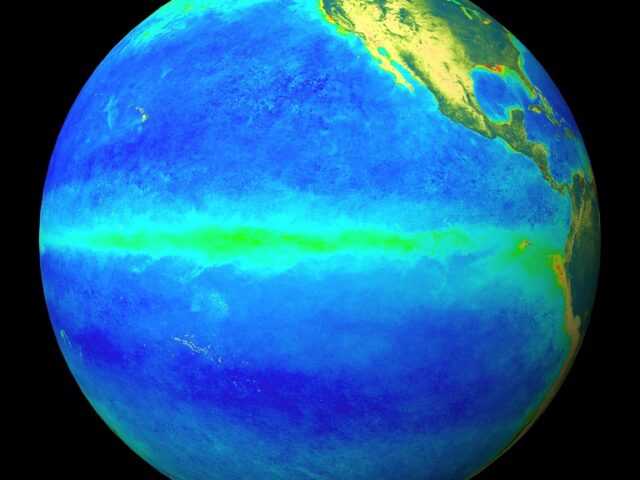
MELBOURNE, Australia – La Niña has become established in the tropical Pacific, the Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) of the Australian Government reports in its latest update. The Bureau’s ENSO Outlook has been raised to La Niña. Climate models suggest this La Niña will be short-lived, persisting until the late southern hemisphere summer or early autumn 2022. La Niña events increase the chance of above average rainfall across much of northern and eastern Australia during summer.
Several indicators of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) now show clear La Niña patterns. Sea surface temperatures in the tropical Pacific are close to La Niña thresholds, with climate model outlooks expecting them to cool further. In the atmosphere, cloud and wind patterns are typical of La Niña, indicating the atmosphere is now responding to, and reinforcing, the changes observed in the ocean.
The negative Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) is approaching its end, with oceanic index values in the neutral range. However, cloud and wind patterns across the eastern Indian Ocean suggest some IOD influence remains. All models indicate the IOD will remain neutral for the coming months, consistent with its typical seasonal cycle. A negative IOD increases the chances of above-average spring rainfall for much of southern and eastern Australia.
The Madden–Julian Oscillation (MJO) is currently over the Maritime Continent region at weak to moderate strength. The MJO is forecast to progress eastwards across the Maritime Continent and into the western Pacific over the coming fortnight, increasing the chances of above average rainfall across northern Australia and the Maritime Continent, to Australia’s north.
The Southern Annular Mode (SAM) has generally been positive for several weeks. It is forecast to remain at positive levels to the end of the year. A positive SAM during summer typically brings wetter weather to eastern parts of Australia, but drier than average conditions for western Tasmania.
Climate change continues to influence Australian and global climate. Australia’s climate has warmed by around 1.44 °C for the 1910–2019 period. Rainfall across northern Australia during its wet season (October–April) has increased since the late 1990s. In recent decades there has been a trend towards a greater proportion of rainfall from high intensity short duration rainfall events, especially across northern Australia.