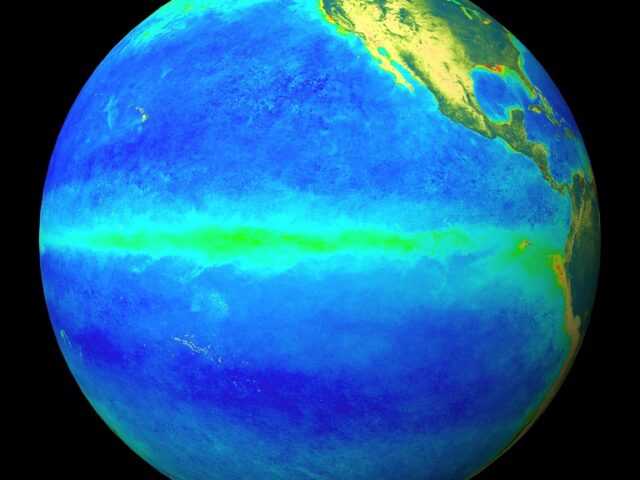
While the 2015–16 El Niño remains at weak to moderate levels, recent changes in the tropical Pacific Ocean and atmosphere, combined with current climate model outlooks, suggest the likelihood of La Niña forming in 2016 has increased to around 50%. As a result, the Bureau’s ENSO Outlook status has moved to La Niña watch.
Temperatures below the Pacific Ocean surface have declined since late 2015, with all but the top 50 metres now cooler than normal. At the sea surface, temperatures have cooled by over 1 °C since their peak, but remain warmer than average and still at El Niño levels.
The Southern Oscillation Index and trade winds also show clear signs that El Niño is in decline. The SOI has recently risen to near-neutral levels, while trade winds are near normal. However some indicators, such as cloudiness near the Date Line, have shown only a limited shift away from El Niño patterns.
International climate models suggest El Niño will continue to weaken during the southern autumn, returning to neutral levels by mid-2016. By spring, five of the eight surveyed models suggest La Niña is likely, with three remaining neutral.
ENSO forecasts made at this time of year tend to have lower accuracy than at other times, with a clearer picture to emerge over the coming months.
La Niña is often, but not always, associated with above-average winter-spring rainfall over northern, central and eastern Australia.
Australia’s climate is also being influenced by record warm temperatures in the Indian Ocean. The warmth in the Indian Ocean will likely provide extra moisture for rain systems as they cross Australia during the southern autumn